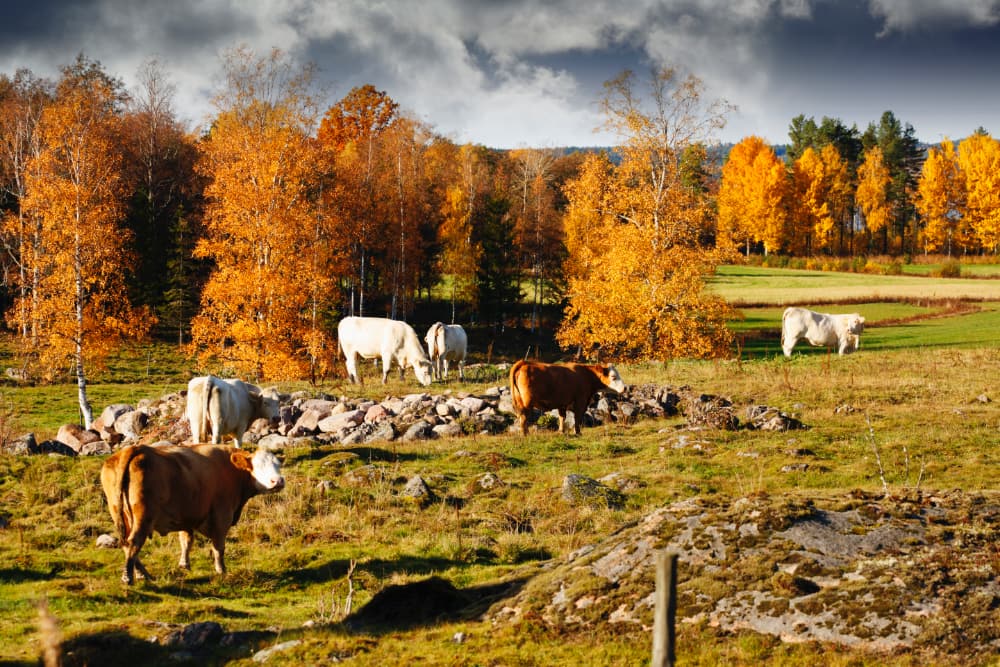
A silvopasture should always be an intentional integration on working farms. If farms are not currently using this type of on-farm management, they may want to start sooner than later. Silvo pasture has long been a form of agroforestry, which is a term that began back in the 1970s. Today, we will be discussing the silvopasture definition. As well as how it can benefit farms all over the world.

What is Silvopasture?
The silvopasture definition is basically an integration of trees and forages within working farms. Silva is a Latin term. It simply refers to the trees within a region. The term pasture refers to a parcel of land that has been devoted to grazing livestock.
All silvopastures should be completed intentionally. The goal of this farming technique is to create both timber production and livestock production in the same area.
All silvopastures have trees that create between 30% and 40% shade. Forages that tolerate shade should also be included in a silvo pasture. The result is then a shaded pasture that livestock can roam in freely out of the summer sun.
It is possible to create a silvopasture in a wooded area or in a pasture. Silvopastures have even been created in orchards. It takes quite a bit of work to change all these areas into a silvo pasture. However, the result will benefit the landowner in numerous ways.
Location Dependent Silvopasture Trees and Forage Plants
Northwest
In the Northwest, it is best to plant ponderosa pine, Douglas fir, black walnut, maple, poplar, and red alder trees. As for forage plants, tall fescue, orchard grass, white clover, and ryegrass are the best options for these silvopastures.
Northeast
Over in the Northeast, hardwood trees and larch trees are better options for a silvo pasture. The best plants include Kura clover, reed canary grass, eastern Gama grass, and bluegrass provide better results.
Southwest
Out in the Southwest, ponderosa pine, nut trees, and Douglas firs are best. Although, hardwood trees and longleaf pines work well in the state of Texas. As for plants, it is all about the cool and warm season grasses in this area of the country.
Southeast
All types of pine trees work well in the Southeast for silvopastures. Bahia grass and crimson clover are the better plants for foraging. However, as you continue to move to the northern regions of the Southeast, this all changes. The northern areas prefer nut trees, black locust, and white pine trees. As for plants, red clover, orchard grass, and white clover are excellent forage bases.
See how Nexton is using hydroponic systems in farming.
Benefits of Managing a Silvopasture
- Creates a Cool and Comfortable Environment for Livestock
All livestock spend the hottest days of the year searching for shade, so they do not overheat. All animals can die from heat stress if the conditions are just right. It takes really extreme temperatures for this to happen to goats, bison, and cattle. However, pigs cannot sweat. Therefore, they can easily overheat in a short amount of time.
During colder and inclement weather, a silvopasture can also be helpful. The trees will block some of the stronger winds. Hail and torrential downpours won’t be as bad under the trees either. While it is always best to bring animals in during inclement weather, silvopastures can be helpful for those storms that seemingly come out of nowhere.
- Faster Timber Growth Rates Plus Timber with Better Value
Silvopastures benefits the timber industry in two ways.
Since this is a pasture, the timber will be fertilized more often. Some of the fertilizer will be what is used on the plants that will be foraged. The other fertilizer will come from the animals that graze in these pastures. Their manure will automatically fertilize everything in the area.
Since the livestock will be in this area grazing, it is necessary to make sure all unnecessary limbs and branches are trimmed. This will ensure the animals do not graze on them. Trimming those parts of the trees will create more valuable timber. Plus, this step makes the trees grow faster.
Since the trees can be felled sooner, there is a shorter forest rotation in every silvo pasture.
- Creates Better Nutrition for Grazing Animals
The plants that are used in silvo pastures are more nutritious for livestock compared to plants that are used in sunnier areas. Depending on where a silvopasture is located, edible trees and shrubs can also be planted. Leucaena trees are one of the best options, especially for grazing cattle. Any dairy cattle that eat from those trees have increased milk production.
- Increased Income
We already spoke about better quality timber, which brings in more money. However, these types of pastures will also help raise better livestock. When the two are combined, it means increased income.
A few other benefits include improved water quality, increased wildlife diversity, and better soil. Add in less soil erosion from wind and water and the result is a space that is safer for livestock to roam.
Tips for Management of a Silvopasture
There are a few tips everyone can use to create the best silvopastures possible on their land. They include:
- Intensive rotational grazing, modest stocking, and monitoring of the pasture is essential.
- Consider the susceptibility of saplings and seedlings to browsing to avoid decreased foraging.
- Trim and prune trees as necessary to ensure better quality timber.
- Consider the livestock grazing in the pasture and avoid any trees and plants that could be poisonous to certain species.
Now that you know the silvopasture definition, you may realize you have seen these types of pastures in the past. You will definitely be seeing more silvopastures in the future. Especially as landowners begin to realize how they can benefit from multiple income streams. If you want to start a silvo pasture on your land, you now have the information to help you get started.